Patients with bone and joint problems are always looking for the best orthopaedic surgeon in Nasr City to treat bone problems and diseases such as fractures and torn ligaments, as well as to perform knee arthroscopy and joint replacement surgery.
In this context, choosing an excellent orthopaedic surgeon is one of the most important points to focus on when looking for the best orthopaedic surgeon in Nasr City.

How to choose the best orthopaedic surgeon in Nasr City?
To choose an excellent orthopaedic surgeon in Nasr City, here are the main factors to consider
- The institutions and hospitals where the doctor works:
- Dr. Ibrahim Sharawi works in some of the largest hospitals in Cairo and the United States, such as Cleopatra Hospitals, Saudi German Hospital, Ain Shams University, and Ohio University in the United States. This qualifies him to be one of the best orthopaedic surgeons in Cairo and the one of the most skilled orthopaedic surgeons in Egypt.
- Review of academic qualifications:
- It is essential to verify Dr. Sharawi’s qualifications, credentials, courses, and academic degrees, including his specialisation in orthopaedic surgery and knee surgery.
- Commitment to continuing medical education:
- This includes attending conferences and scientific meetings. Dr. Sharawi points out his regular attendance at these events and his contribution by giving lectures in the specialities of microsurgery.
- Patient reviews: Patient reviews are a testament to the doctor’s success in the two most important steps in treatment, which are effective communication and a successful treatment plan.
- Experience in complex bone and joint surgeries
- Dr. Ibrahim Sharawi is an expert in complex orthopaedic surgeries, including knee and shoulder joint surgeries, making him an excellent choice for those looking for the best knee specialist in Nasr City.
What are the most common conditions treated by an orthopaedic surgeon?
An orthopaedic surgeon treats a wide range of conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system. These problems are usually divided into two main categories: diseases that affect the bone structure itself, and diseases and injuries that affect the surrounding joints and ligaments. The following is a breakdown of the most important of these conditions:
First: Common bone diseases
- Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is known as the “silent disease” because it can develop without pain until a sudden fracture occurs. It is a condition in which the bone loses its density and strength, making it porous and susceptible to fracture from the slightest effort or minor fall.
Common symptoms: There are usually no early symptoms, but as the condition progresses, persistent back pain (due to compression fractures of the vertebrae), shortening of stature over time, and curvature of the spine may occur.
Treatment: Treatment with the best orthopaedic surgeon depends on early diagnosis through bone density measurement every five years after the age of 60
(DEXA scan). The treatment plan includes calcium and vitamin D supplements, bone-strengthening medications (such as bisphosphonates) and osteoporosis injections every six months, lifestyle changes, and weight-bearing exercises to strengthen the bones.
- Rickets and Osteomalacia
Rickets (in adults) or osteomalacia (in children) is a condition that often results from a severe and persistent vitamin D deficiency, which prevents bones from hardening and mineralising properly, making them soft and weak.
The most common symptoms: In children, there is a noticeable bowing of the legs (knees turned inwards or outwards), delayed walking and growth. In adults, the patient complains of general pain in the bones and joints, muscle weakness, and difficulty getting up from a sitting position.
Treatment: The primary treatment is to compensate for nutritional deficiencies through therapeutic doses of vitamin D and calcium under medical supervision, and safe exposure to sunlight. In cases of severe deformities in children, we may resort to surgical intervention to correct the bones.
Second: Joint diseases and injuries
- Knee osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis is one of the most common bone diseases and occurs as a result of erosion of the cartilage lining the joint surface, leading to friction between the bones.
The most common symptoms are pain that increases with movement and climbing stairs, stiffness in the knee upon waking up, swelling, and a “cracking” or rubbing sound during movement.
Treatment: Treatment begins conservatively (weight loss, physical therapy, local injections such as hyaluronic acid or plasma). In advanced cases that do not respond to treatment and affect daily life, knee replacement surgery is a radical and successful solution to restore pain-free movement.
- Meniscus tear
The meniscus is a crescent-shaped cartilage “cushion” that absorbs shock within the knee. Tears often occur as a result of sudden twisting movements during sports or as a result of wear and tear with age.
Common symptoms: sudden pain, rapid swelling, a feeling that the knee is “locked” or cannot be fully extended, and sometimes a feeling of instability.
Treatment: Treatment depends on the location and size of the tear. In a few cases, small tears are in the blood supply area and may heal with rest and physical therapy. Larger tears or those that cause the knee to “lock” require arthroscopic surgery to trim or stitch the cartilage, which is a precise procedure with a very high success rate.
- Anterior cruciate ligament tear (ACL tear)
This is a very common injury among athletes and football players, and occurs as a result of sudden stops and changes in direction, leading to a tear in the ligament responsible for knee stability.
The most common symptoms are hearing a “pop” at the time of injury, severe swelling within hours, sharp pain, and most importantly, a feeling of “instability” or that the knee is giving way when trying to walk or run.
Treatment: Conservative treatment may be suitable for people over 60 years of age who are less active. However, for young people and athletes, arthroscopic cruciate ligament reconstruction is necessary to restore knee stability and prevent premature degeneration in the future, followed by a rigorous rehabilitation programme.
- Rotator Cuff Tear
A tear occurs in the rotator cuff, which is a group of tendons and muscles that surround the shoulder joint and allow the arm to be raised and rotated. The tear may be partial or complete.
Common symptoms: Deep pain in the shoulder that worsens at night and prevents sleeping on the affected side, severe weakness in the arm, and difficulty raising the hand above the head or combing the hair.
Treatment: In cases of complete rupture or failure of conservative treatment, surgical shoulder arthroscopy is performed to suture the torn tendon and secure it in place using microtacks.
- Recurrent Shoulder Dislocation
Since the shoulder joint is the most mobile joint in the body, it is the most prone to dislocation (the head of the humerus bone coming out of the socket). After the first dislocation, the likelihood of recurrence increases.
Common symptoms: obvious deformity of the shoulder at the time of dislocation, severe pain, and inability to move the arm. Patients with recurrent dislocation are always apprehensive and afraid to use their arm in certain positions.
Treatment: Acute dislocation requires immediate joint reduction. To prevent recurrence, surgery (often arthroscopic) is performed to repair the torn ligaments (Bankart Repair) and stabilise the joint, allowing the patient to resume their daily activities and sports with confidence.
Book Your Consultation Now
Take the first step towards recovery. Contact us directly via phone or WhatsApp to schedule your appointment.
What surgical procedures does an orthopaedic surgeon perform?
Orthopaedic surgeons perform a wide range of surgical procedures, ranging from minor arthroscopic procedures to major surgeries to repair fractures. Below is a breakdown of the most important procedures and the techniques used in them:
- Arthroscopic cruciate ligament surgery (ACL reconstruction)
This procedure is considered the gold standard for treating anterior cruciate ligament tears, especially in athletes and young people. The torn ligament is not “stitched” because it does not heal, but rather “reconstructed” using a replacement tendon graft.
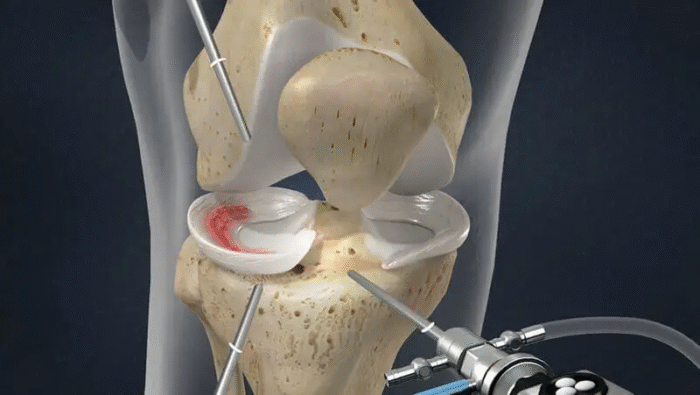
What are the best types of tendon grafts for ACL reconstruction?
The choice of graft depends on the patient’s age, level of athletic activity, and whether a graft has been taken from one of the tendons before. The most common types are:
- Hamstring Tendon Autograft:
- Description: Two tendons are taken from the hamstring (back) of the thigh through a small incision (2 cm).
- Advantages: Currently the most common type. Characterised by less pain after surgery, better cosmetic appearance, and excellent stability.
- Disadvantages: There may be slight weakness in the hamstring, but this improves with rehabilitation.
- Patellar Tendon Autograft:
- Description: The middle third of the patellar tendon is taken along with a small piece of bone from the patella and tibia.
- Advantages: Considered the “gold standard” for professional football players and high-impact sports because it fuses (bone to bone), providing very strong and rapid stability.
- Disadvantages: May cause pain in the front of the knee when prostrating or kneeling for long periods, and the incision is slightly larger.
- Quadriceps tendon:
- Description: A portion of the tendon from the front of the thigh above the kneecap is taken.
- Advantages: Its use has recently increased because it is thick and strong, and it is an excellent choice for revision ACL surgery.
- Artificial or allograft grafts:
- These are usually used for older people or in cases of multiple ligament injuries, as we do not have to take tendons from the patient’s own body, which reduces the duration of the operation and pain, but they are more expensive and heal slightly slower.
- Meniscus Surgery
The meniscus acts as a “shock absorber” in the knee. When a tear occurs, the surgeon determines the type of surgery based on the location of the tear (is it supplied with blood or not?) and the patient’s age.
- Partial Meniscectomy:
- When is it used? In cases of torn meniscus, tears in the white area (which does not receive blood and therefore does not heal), or in older patients (with associated roughness).
- Procedure: The surgeon removes only the torn part that is causing pain or locking of the knee, leaving the rest of the healthy cartilage intact.
- Advantages: Very quick recovery (the patient can walk immediately after the operation).
- Meniscus repair:
- When is it used? In cases of recent tears, longitudinal tears in the red zone (rich in blood), and in young people and athletes.
- Procedure: Preservation of the cartilage and reattachment using “hooks” or fine sutures with an arthroscope.
- Advantages: Preserves cartilage function and protects the knee from future stiffness. However, it requires a longer rehabilitation period (full weight-bearing on the knee may be prohibited for several weeks).
- Fracture fixation: comparison between intramedullary nails, plates and screws
The best Orthopaedic surgeon in Nasr City-Cairo uses different techniques to fix fractures to ensure proper healing. The choice depends mainly on the location of the fracture and the type of bone.
| Feature | Intramedullary Nail (IM Nail) | Plate & Screws (ORIF) |
| Implant Location | Inserted inside the hollow center of the bone (medullary canal). | Fixed onto the outer surface of the bone. |
| Incision Size | Minimally invasive; requires small incisions away from the fracture site. | Requires a long open incision to expose the bone and fracture site. |
| Effect on Healing (Biology) | Preserves the fracture hematoma (blood clot), which accelerates natural healing. | Requires stripping the periosteum (bone covering) and cleaning the site, which may disturb the local blood supply. |
| Weight Bearing | Allows for early weight-bearing and walking (Load Sharing). | Usually requires delayed weight-bearing until healing signs appear (Load Bearing). |
| Best Indications | Fractures in the middle (shaft) of long bones (e.g., Femur, Tibia). | Fractures near joints (articular surfaces) or complex comminuted fractures. |
| Biomechanical Principle | Load Sharing (The nail shares the body weight with the bone). | Load Bearing (The plate carries the weight instead of the bone). |
4- Bone tumour surgery
Dr Ibrahim Shaarawi is one of the few specialists in Egypt and the Arab world who specialises in bone and joint tumour surgery, as bone tumour surgery requires a high level of skill that not all orthopaedic surgeons possess.
In the past, amputation was the only solution for bone cancer. Today, with the development of surgical techniques used by the best bone tumour doctors, we are able to completely remove the tumour while preserving the limb (limb salvage) in more than 90% of cases, with reconstruction of the missing part so that the patient can return to their normal life.
The operation is divided into two stages: safe removal, then reconstruction. Removal with wide safety margins is the basis for treating bone tumours and cancerous tissue to ensure complete removal of the tumour and all surrounding tissue.
After removing the tumour with “safety margins” to ensure that it does not return, a large bone gap is formed, which is compensated for in one of the following ways:
- Artificial joints for tumours (Megaprosthesis / Tumour Prosthesis):
Description: These are special metal joints that differ from normal joints. They consist of modular pieces of different lengths and sizes that are assembled in the operating room to compensate for any lost bone length (whether 5 cm or the entire femur).
Best uses: Malignant bone tumours close to joints (such as the knee, thigh, shoulder) and for patients who need to regain mobility quickly.
Major advantage: Immediate stability (the patient can walk on it after a few days).
Disadvantage: There is high pressure on prosthetic joints of this type as they bear the pressure of the joint surface, the surrounding ligaments, and the resected bone, leading to relatively high complication rates compared to primary joints. These joints are also expensive compared to other prosthetic joints. - Biological Reconstruction: This involves replacing the lost bone with natural bone rather than metal, and there are several methods:
Bone grafts from a donor (Allograft): Using bones from a bone bank to replace the lost part. The advantage here is that the bone heals with the patient’s bone and becomes part of it.
Fibula graft: Taking the fibula (from the patient’s own leg) with its blood vessels and transplanting it to the site of the resected bone (using microsurgery).
Exhaustive Bone Recycling Technique (ECRT): A highly advanced technique in which the tumour-affected bone is removed, then treated (with radiation or liquid nitrogen) to completely kill the cancer cells, and then reinserted into the patient’s body to act as a support.
Dr. Sharawi is considered an expert in biological reconstruction techniques in Egypt and the Arab world, aiming to use methods that do not rely on artificial parts in bone reconstruction.
Who is the best orthopaedic surgeon in Nasr City?
- According to his patients and many medical professionals, Professor Ibrahim Sharawi is considered the best orthopaedic surgeon in Nasr City.
He is a pioneer in the field of advanced and complex orthopaedic surgery.
Why choose Dr Ibrahim Sharawi?
When you choose Dr. Ibrahim Sharawi, you are choosing
- Modern American expertise in orthopaedics and joint surgery from Ohio University Hospitals
- Intensive training at the largest university hospitals in Egypt and the Middle East
- Highly successful testimonials from a large number of patients who have placed their trust in Dr. Sharawi.
- Dr. Ibrahim Sharawy currently works as a teacher and consultant in orthopaedic surgery, joints, and tumours at Ain Shams University Hospitals, as well as a visiting professor of orthopaedic surgery at Ohio University Hospitals in the United States. He performs his operations in several major hospitals in Cairo and Egypt, where he makes regular visits to some governorates in Egypt to draw on his expertise in treating complex cases.
Certificates obtained by the best orthopaedic surgeon in Nasr City:
Dr. Ibrahim Sharawi has obtained several certificates and courses in this precise field from Ohio University in the United States and the Cochrane Research Foundation in the United Kingdom. This is in addition to his intensive training at Ain Shams University Hospitals, Ohio University Hospitals, and Nashon Wade Hospital, which qualifies him to perform the most difficult and complex operations restrictive, such as hip replacement, knee replacement, and the removal of all types of malignant and benign tumours with the reconstruction of bones and tissues using the latest methods.
All this experience has made him one of the best orthopaedic surgeons in Nasr City and Cairo.
What is the address of the best orthopaedic clinic in Nasr City?
Dr. Ibrahim Sharawi’s clinic is located in a vital and upscale location in Cairo, between the Nasr City and Heliopolis neighbourhoods,Near common Landmarks like City stars Mall and Abbas Elakkad Street making it easily accessible to all patients.
Services provided by the best orthopaedic clinics in Nasr City:
The best orthopaedic clinics in Nasr City provide specialist examinations as well as most orthopaedic procedures, which are listed below:
The Best Orthopaedic clinic in Nasr City offer exceptional services, including specialist diagnosis and surgery for a wide range of bone problems and injuries. Here is an overview of the services offered by these clinics:
joint and tendon injections to effectively treat bone problems without the need for surgery.
Follow-up care for orthopaedic patients and rehabilitation
In addition, the best orthopaedic doctors in Nasr City offer specialised services in the treatment of bone and joint problems, including:
- Conservative treatment of fractures, including the use of casts or splints to stabilise bones.
- Correction and repair of meniscus tear under spinal anaesthesia, which helps restore knee function.
- Knee replacement using an artificial joint to treat cartilage problems and improve knee movement.
- Cruciate ligament repair surgery and sports injury surgery to restore knee stability, reduce pain and improve function.
- Shoulder and hand surgeries, including shoulder arthroscopy to effectively resolve shoulder problems without the need for traditional surgery.
- Hip replacement surgery to restore hip movement and reduce pain.
- Ankle fusion surgery to improve ankle stability and reduce pain and swelling.
- Achilles tendon surgery to reduce the risk of rupture.
- In addition, many complex conditions are treated, such as benign and malignant bone tumours, bone deformities and bone curvature in children and adults. All these services are provided by a team of specialised and skilled doctors to ensure comprehensive and high-quality care for patients.
